Ever wonder if odors in the air are actually particles floating around and up your nose? Well they are, of course they are. Volatile Organic Compounds, or VOCs, are organic emissions from products we use every day. Some have distinct odors, or aren’t concentrated enough for the average nose to detect, and others are completely odorless.
Something as simple as cleaning your kitchen counter with a chemical cleaner releases VOCs into your home’s air, and a high level of VOCs could mean serious health threats to you and your family. Using an indoor air quality meter, or VOC meter can help ensure you maintain a safe environment at home.
VOCs Explained
Volatile Organic Compounds are used in the manufacturing processes of most consumer chemical products, but what are VOCs really? Well for starters, that daisy-fresh scented laundry detergent your mom loves so much contains VOCs, as do paint, cleaners, detergents, polishes, makeup, automotive liquids, pesticides….nearly everything that’s bottled for household use can potentially contain VOCs.
But wait, there’s more, Johnny! Printing, dry-cleaning, permanent markers, crafting, remodeling, and – heck – even some furniture can emit VOCs.
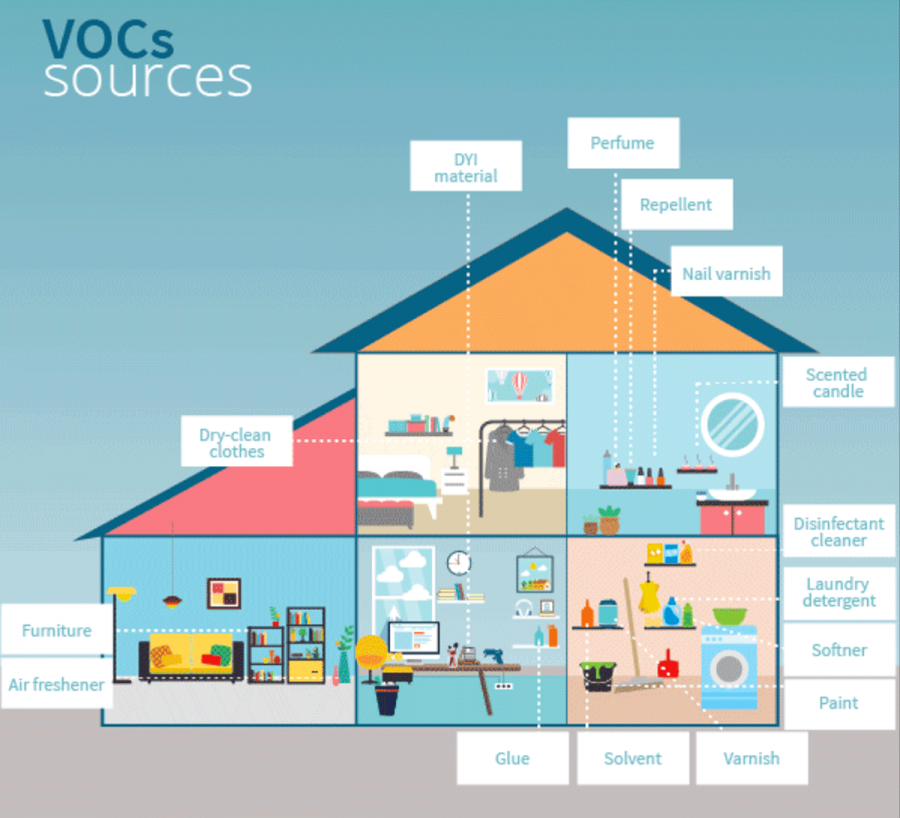
So what’s the risk? I mean if everybody’s doing it…
Well, everyone definitely has VOCs in their home, but they may not be inhaling furniture polish in the pantry like you.
Banter aside, health risks are substantial when VOC levels of certain pollutants exceed healthy limits. The EPA estimates that homes contain an average of two-to-five times as many VOCs as outdoor environments, and home owners often expose themselves to unsafe containment levels when performing daily tasks without even realizing it.
Another issue is that while elevated concentrations will eventually dissipate overtime, many homes and buildings lack adequate ventilation to disperse the fumes effectively, resulting in emitted VOCs lingering much longer, and increasing exposure and health risks. There’s a commonly uttered phrase in the HVAC industry, called sick building syndrome, used to describe an office environment in which workers are ill or call in sick more frequently than management expects, almost always caused by – you guessed it – poor ventilation which inhibits pollutant filtration, leading to prolonged exposure to VOCs.
VOCs can cause all kinds of nasty health effects, including but not limited to:
- Headaches
- Irritation to eyes, nose, and throat
- Skin reactions
- Nausea
- Fatigue
- Dizziness
- Liver damage
- Kidney damage
- Cancer
So what’s the first step in eliminating VOCs? Measurement. You must first understand your level of exposure before you can improve indoor air quality. To do this, you can either purchase a VOC meter, or look for VOC meter rental services to take readings in your building of choice.
Using an indoor air purifier that’s designed to adsorb VOCs can help filter out many of the harmful pollutants that would otherwise linger in your air. Another good practice is to ensure that your home is well-ventilated. Open windows and doors to air out tight spaces as an immediate solution, and keep temperature and humidity regulated to ensure VOC off-gas isn’t released through chemical reactions caused by rising temperatures.
How Do VOC Meters Work?
So what is a VOC monitor? Photo-Ionization Detection (PID) is the most commonly used technology to calculate VOC content in the air. Sound like gibberish? Let me break it down for you:
An illustration of a VOC meter detecting pollutants in the surrounding air.
When air enters the end of a VOC meter, a UV light interacts with the molecules in the air. Organic compounds release positively charged ions when they pass through the light, which are then captured by a negatively charged plate producing a measurable electrical current. The current is measured by the PID device, which is then used by the VOC sensor to determine the type and quantity of the detected VOCs. The higher the electrical current, the more pollutants in the air, and the UV lamp used by the manufacturer of the VOC meter determines what contaminants can be detected by the VOC sensor.
Who Uses VOC Meters?
What is VOC monitoring? VOC meters are used by a wide variety of people for both personal and professional purposes. HVAC and indoor air quality experts routinely use VOC monitors to detect pollutant concentrations in buildings, using that information to develop an air quality plan for customers. Typically, professionals will examine environments for VOC sources to see if a root cause of pollution can be minimized, or eliminated. Afterwards, the contractor will follow up with routine inspections to report any progress back to the customer.
Individuals can also use VOC meters to measure pollutants in their homes. People with allergies, constant headaches, sinus irritation, asthma, or any breathing disabilities can greatly benefit from routine VOC measurement.
What Are Average VOC Levels in Households?
Using a VOC tester is only part of the battle, though. What you really need to know is how to read its findings. VOC measurements will typically be displayed in parts per million (ppm), or parts per billion (ppb).
While a reading of complex compounds from multiple VOCs are common, and obtaining a definitive answer regarding “average” indoor VOC levels is difficult (if not impossible), there are some simple rules to adhere to in order to ensure that you’re doing your part to reduce volatile pollutants in your home. Generally speaking, VOC readings less than 1,ooo ppb (1.0 ppm) shouldn’t cause adverse health effects. Prolonged exposure to contaminants between 1,000 and 10,000 ppb can cause mild health issues, and exposure to pollutants exceeding 10,000 ppb may produce significant issues with continued exposure.
But keep in mind these are just simple guidelines, without analyzing the specific VOCs in your environment it’s difficult to say how you could react. Detailed VOC analysis is a service that’s available if you’re interested (check with local HVAC companies), but it’s usually costly and inconvenient.
Using a handheld VOC meter can be just as effective at determining levels of pollutants in your home. Understand though that consumer-grade VOC meters will test for what’s called the TVOC, or the Total VOC, to give testers an overall indication of the environment’s condition – as opposed to identifying individual VOC levels. That said, this should be more than sufficient for most consumers out there.